Sarah Wittmann, M. Mangir Murshed, Kowsik Ghosh, Aylin Koldemir, Rainer Pöttgen, Cecilia B. Mendive, Thorsten M. Gesing
Journal of the American Ceramic Society (2024): e20170
https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.20170
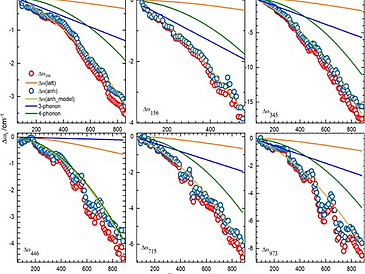
We report on temperature-dependent structural and spectroscopic properties of two new members of the mullite-type ceramics SnAlBO4 and SnGaBO4. In-situ X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) demonstrates positive thermal expansion behavior for all orthorhombic lattice parameters between 13 and 840 K. The lattice thermal expansion is modeled by Grüneisen first-order approximation, where the vibrational energy is calculated by the Debye–Einstein–anharmonicity (DEA) approach. Although the thermal changes of the metric parameters do not show any discontinuity, the double-Debye model and low-temperature thermal analysis leave hints for subtle displacive changes. Splitting of the tin-doublets of the 119Sn Mössbauer spectra at low temperature is assumed to be associated with structural modulation although the temperature-dependent Raman spectra could not support these findings. The modulation could either be dynamic which requires much longer thermal equilibration than the speed of the data collection for XRPD and Raman spectroscopy. Selective Raman mode frequencies are analyzed using a modified Klemens model, which helps to understand the thermal anharmonic behaviors of the SnO4, MO6, and BO3 polyhedra as a function of temperature.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of the American Ceramic Society published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Ceramic Society